Alzheimer’s research breakthroughs are revolutionizing our understanding of this devastating neurodegenerative disease. At the forefront of these advancements is neuroscientist Beth Stevens, whose innovative studies on microglial cells reveal critical insights into how the brain’s immune system interacts with neural connections. By understanding the role of these immune cells in the pruning process, researchers are now better equipped to identify new biomarkers for Alzheimer’s, potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and more effective Alzheimer’s treatment options. The implications of Stevens’ work extend beyond Alzheimer’s, offering hope for combating various neurodegenerative diseases that affect millions globally. As we forge ahead into an era of personalized medicine, these breakthroughs represent a beacon of hope for millions of families impacted by Alzheimer’s.
Recent discoveries in the field of Alzheimer’s research have opened new avenues for treatment and diagnosis, particularly through the study of brain immune cells known as microglia. These breakthroughs, spearheaded by leading scientists like Beth Stevens, emphasize the essential role of microglial cells in maintaining neuronal health and their contribution to neurodegenerative disorders. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms behind cognitive decline, they are uncovering novel biomarkers for Alzheimer’s, allowing for a more accurate understanding of disease progression. This progress is critical as experts seek innovative therapies that target the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s, offering hope to those affected. By understanding how immune responses in the brain can lead to detrimental effects, we can pave the way for significant advancements in treating Alzheimer’s and similar diseases.
Understanding Microglial Cells: The Immune Warriors of the Brain
Microglial cells play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the brain by acting as its immune defenders. Unlike other immune cells in the body, microglia reside within the brain and spinal cord, constantly monitoring the environment for signs of inflammation or damage. This proactive surveillance is essential for clearing away cellular debris and damaged neurons, a process vital for maintaining cognitive function and overall brain health. Research conducted by Beth Stevens has revealed just how vital these cells are in the context of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and multiple sclerosis.
However, the balance that microglial cells must maintain between protecting nerve cells and potentially contributing to neurodegeneration is delicate. When microglia become overactive or misdirected, they may inadvertently harm healthy neurons instead of supporting them. This underscores the importance of further research into the mechanisms of microglial activity, as a clearer understanding could pave the way for groundbreaking Alzheimer’s treatments that harness the natural functions of these immune cells.
Alzheimer’s Research Breakthroughs: New Insights from the Stevens Lab
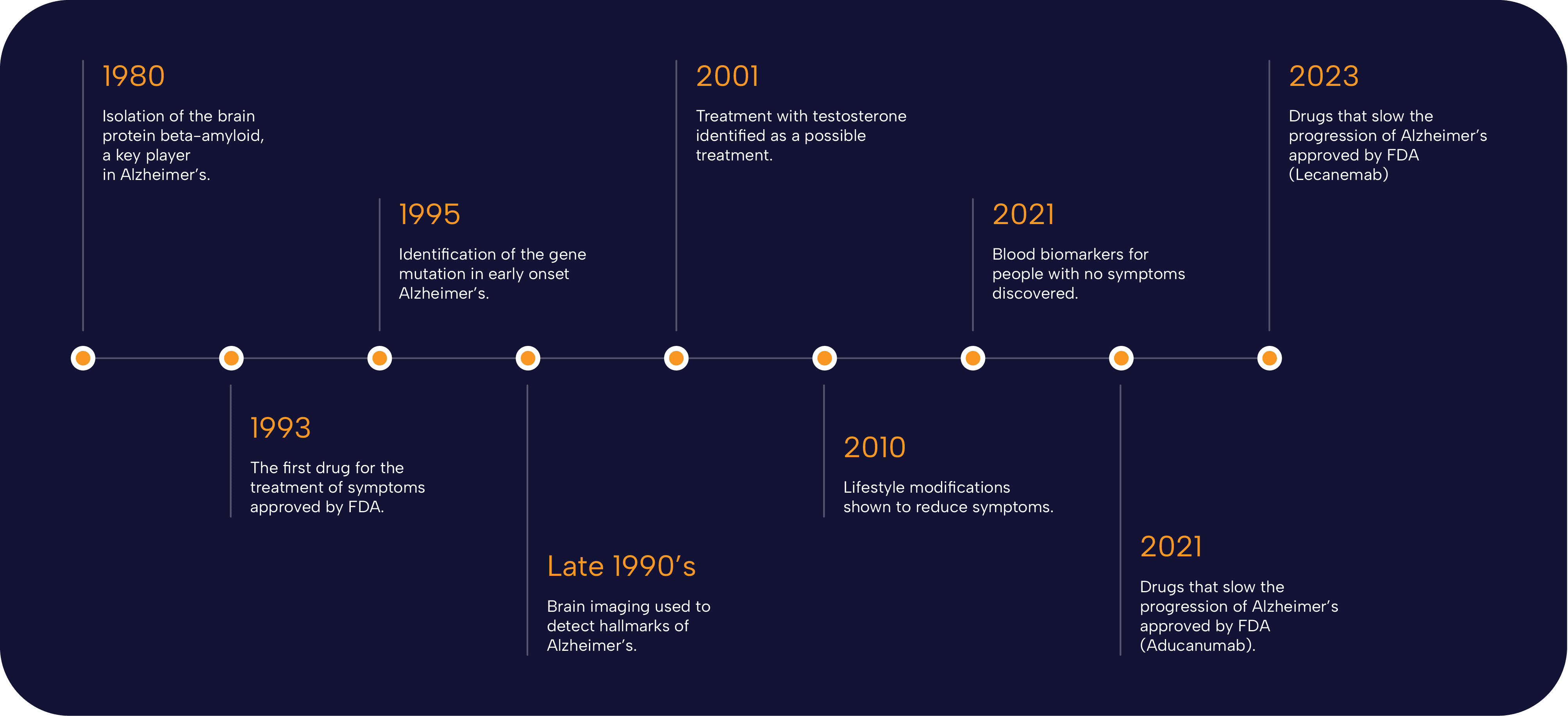
Recent advancements in Alzheimer’s research spearheaded by Beth Stevens and her team have illuminated the complex interactions between microglial function and neurodegenerative processes. By studying microglial cells, researchers have begun to identify potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease, enabling earlier detection and intervention. These breakthroughs are critical, considering the rapid increase in Alzheimer’s cases as the population ages, with projections indicating a doubling of annual cases by 2050. The significance of these discoveries extends beyond mere statistics, as they hold the potential to transform the lives of millions.
Stevens’ work emphasizes the necessity of innovative research methodologies to uncover the underlying biological mechanisms of Alzheimer’s. By utilizing advanced imaging techniques, her lab has been able to observe the behavior of microglial cells in live models, leading to insights that could inform therapeutic strategies. Such inquiries not only enhance our understanding of Alzheimer’s treatment but also inform future research directions that could target other neurodegenerative diseases, ultimately contributing to the development of effective strategies aimed at prevention and care.
The Role of Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease Detection and Treatment
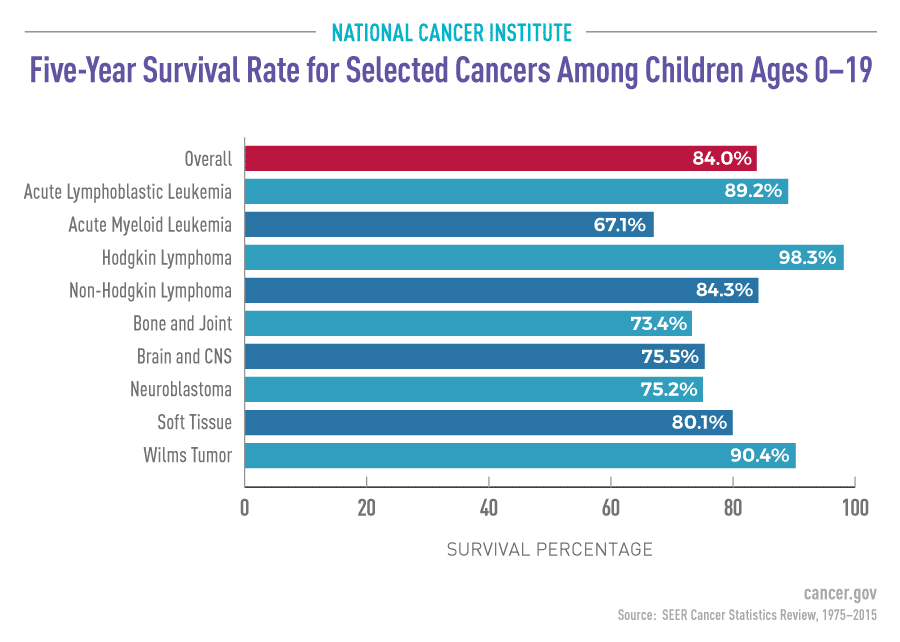
Biomarkers are pivotal in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, as they facilitate the identification of changes in the brain before clinical symptoms appear. Beth Stevens and her collaborators are making significant strides in this area, striving to establish reliable biomarkers that can indicate microglial activity associated with neuroinflammation. The success of such biomarkers could revolutionize Alzheimer’s treatment, allowing for timely interventions that may slow the progression of the disease and improve patient outcomes.
By leveraging the insights gained from studies of microglial cells, researchers hope to develop assays that not only detect Alzheimer’s but also provide insights into other neurodegenerative conditions. This research aligns with the broader goal of personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored based on individual biomarker profiles. Such approaches promise to enhance the precision of Alzheimer’s treatment, fostering a new era in combating neurodegenerative diseases.
Transformative Neuroscience: The Path From Basic Science to Therapeutics
The journey from basic science to the development of therapeutics is often complex, but Beth Stevens’ research serves as a compelling example of how fundamental discoveries can lead to transformative medical interventions. Her pioneering work on microglial cells has provided critical insights into the mechanisms that underlie synaptic pruning and cellular homeostasis in the brain. This foundational understanding is not merely academic; it has practical implications in the search for effective Alzheimer’s treatments that could ultimately enhance quality of life for millions.
Moreover, Stevens’ emphasis on curiosity-driven research highlights a crucial aspect of scientific inquiry: the unpredictable pathways through which innovation occurs. While initial studies may seem tangential to disease applications, they are essential for uncovering the biological complexities of conditions like Alzheimer’s. Fostering an environment that values basic research will remain vital in the ongoing fight against neurodegenerative diseases, offering hope for future breakthroughs in treatment and understanding.
Funding and Support: The Backbone of Alzheimer’s Research
Adequate funding is essential for progress in Alzheimer’s research, as showcased by the support received by Beth Stevens and her lab. Federal agencies, notably the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provide critical resources that enable scientists to pursue high-impact studies in neurodegenerative diseases. This financial backing is not only vital for continuing groundbreaking research but also for fostering collaborations among institutions, which can accelerate the translation of findings into clinical applications.
As the landscape of Alzheimer’s disease research evolves, sustaining and increasing funding levels will be essential. The economic burden of Alzheimer’s is projected to escalate, emphasizing the need for investments in research that can lead to effective treatments and preventive measures. By championing the necessity for funding in science, stakeholders can help secure avenues for innovative research that may change the course of Alzheimer’s treatment and care.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Research and Treatment
As the scientific community delves deeper into the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease, the future of research is poised for exciting advancements. The integration of multidisciplinary approaches—ranging from molecular biology to advanced imaging and computational neuroscience—holds tremendous promise for uncovering new therapeutic targets. Researchers like Beth Stevens are at the forefront of this movement, focusing on microglial cells as potential key players in neurodegenerative pathology.
Moreover, the ongoing development of novel technologies to analyze the brain’s immune responses could shed light on previously unexplored aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. As scientists continue to unravel the intricate relationships between microglial function, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration, the potential to discover transformative treatments becomes increasingly tangible. The commitment to understanding these dynamics may not only lead to improved Alzheimer’s treatments but also enhance our global effort to combat all neurodegenerative diseases.
Curiosity-Driven Science: A Necessity in Alzheimer’s Research
Curiosity-driven science is at the heart of major breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research, with researchers like Beth Stevens exemplifying this ethos. Stevens’ journey, driven by a desire to understand how the brain’s immune system influences disease pathways, has led her to pivotal discoveries about microglial cells and their roles in neurodegenerative diseases. This sort of inquiry underscores the unpredictable yet rewarding nature of scientific exploration, where the most impactful findings often stem from basic research.
This approach not only cultivates a deeper understanding of biological mechanisms but also fosters innovation in the development of Alzheimer’s treatments. By prioritizing curiosity in scientific endeavors, the research community can nurture an environment conducive to discovery and growth. The findings emerging from curiosity-driven studies have the potential to reshape the landscape of Alzheimer’s treatment, offering hope for more effective interventions in the future.
The Aging Population: Addressing the Alzheimer’s Epidemic
The growing prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease, especially among an aging population, is emerging as an urgent public health crisis. According to projections, the number of Alzheimer’s cases may double by 2050, underscoring the pressing need for both research and policy action. Beth Stevens’ research has highlighted the critical need for effective strategies to combat this escalating issue, emphasizing the importance of tailored Alzheimer’s treatments that address the unique biological needs of individuals.
Addressing the Alzheimer’s epidemic requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses research, funding, and public awareness. Collaborative efforts among researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers will be essential in mitigating the impacts of this disease on individuals and families. By leveraging the knowledge gained from current research, including the foundational findings on microglial cells and biomarkers, the field can advance towards solutions that not only improve lives but also alleviate the anticipated strains on healthcare systems.
Challenges in Alzheimer’s Research: Navigating the Unknown
Conducting research on Alzheimer’s disease presents a unique set of challenges, largely due to the complexities of the human brain and the multifactorial nature of neurodegeneration. For scientists like Beth Stevens, navigating these challenges requires innovative thinking and resilience. The paradox of Alzheimer’s research lies in the need to understand a condition while the underlying causes often remain elusive, demanding constant adaptation and exploration of new hypotheses and methodologies.
Furthermore, the translation of research findings into effective treatments is a prolonged and uncertain process, often hindered by the intricacies of neurobiology and the regulatory environment. Nonetheless, ongoing research and discoveries concerning microglial function and disease biomarkers have opened new doors for potential therapies. By remaining dedicated to overcoming these challenges, researchers can contribute to the body of knowledge necessary for developing impactful interventions against Alzheimer’s.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research by Beth Stevens?
Beth Stevens has made significant breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research by transforming our understanding of microglial cells. Her lab has discovered that these cells, which act as the brain’s immune system, can improperly prune synapses, contributing to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. This research paves the way for new medications and early detection biomarkers for Alzheimer’s.
How do microglial cells impact Alzheimer’s treatment based on recent research?
Microglial cells play a crucial role in Alzheimer’s treatment as revealed by Beth Stevens’ research. These cells clear away dead or damaged neurons and prune synapses, but improper functioning can lead to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Understanding microglial behavior is vital for developing effective treatments and biomarkers for Alzheimer’s.
What role do biomarkers for Alzheimer’s play in current research breakthroughs?
Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s are essential in current research breakthroughs as they enable earlier detection of the disease. Beth Stevens’ research into microglial cells has identified potential biomarkers that help diagnose Alzheimer’s more effectively, allowing for timely intervention and better management of the disease.
Why are discoveries related to microglial cells significant for neurodegenerative diseases?
Discoveries related to microglial cells are significant for neurodegenerative diseases because they reveal how these immune cells affect brain health and disease progression. Beth Stevens’ work highlights the connection between microglial cell activity and conditions like Alzheimer’s, paving the way for innovative therapies and improved understanding of these diseases.
What is the impact of aging populations on Alzheimer’s research advancements?
The aging population significantly impacts Alzheimer’s research advancements, as the number of cases is projected to rise sharply. With the expected doubling of Alzheimer’s cases by 2050, research led by scientists like Beth Stevens is critical. Their breakthroughs in understanding microglial cells and neurodegenerative diseases aim to address this impending healthcare crisis.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Role of Microglial Cells | Microglia act as the brain’s immune system, clearing damaged cells and pruning synapses. |
| Discovery by Beth Stevens | Beth Stevens’ research indicates that improper pruning by microglia contributes to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Location of Research | The Stevens Lab is based at Boston Children’s Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. |
| Impact of Research | Stevens’ findings could lead to new medications and biomarkers for early detection of Alzheimer’s. |
| Future Projections | With the aging population, Alzheimer’s cases could double by 2050, raising caregiving costs significantly. |
| Funding Support | Stevens’ work was predominantly funded by the National Institutes of Health and other federal agencies. |
| Importance of Basic Science | Basic science and curiosity-driven studies are essential for advancements in understanding and treating diseases. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s research breakthroughs have significantly advanced our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases. The work of Beth Stevens on microglial cells demonstrates the crucial role of the brain’s immune system in maintaining neuronal health and function. By investigating how microglia prune synapses during development, Stevens has uncovered critical insights into how improper microglial activity contributes to Alzheimer’s disease. Her research not only paves the way for innovative treatments and early detection methods but also underscores the importance of foundational research driven by scientific curiosity. As the prevalence of Alzheimer’s is projected to increase, such breakthroughs are vital for addressing the growing healthcare challenges.