The U.S. health innovation ecosystem stands as a pinnacle of global achievement in medical research and technological advancements. Born from the urgent demands of World War II, this dynamic landscape has thrived on a robust foundation of federal funding for research and public-private partnerships. Historically, the impact of WWII on medicine necessitated groundbreaking biomedical research partnerships that transformed military healthcare and set the stage for future innovations. As countless scientists collaborated in this unprecedented effort, they laid the groundwork for a collaborative scientific environment that efficiently fosters ongoing discoveries. Today, this vibrant ecosystem continues to evolve, embodying a legacy of scientific research collaboration that positions the U.S. as a leader in health innovation.
The American health innovation framework represents a comprehensive network of academic, governmental, and industrial collaborations that fuels groundbreaking advancements in medicine. Tracing its roots back to critical wartime initiatives, this innovative model has consistently harnessed federal support to propel biomedical exploration and development. The legacy of the conflict has indelibly shaped the trajectory of healthcare technologies, emphasizing the necessity of coordinated efforts between diverse sectors. Throughout its history of health innovation, the U.S. has emerged as a beacon of progress, showcasing the potential of integrated scientific inquiry and collaboration. This synergistic approach not only enhances the country’s healthcare system but also serves as a blueprint for global health innovation.
The Origins of the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem has its roots embedded in the urgency of World War II, where scientific breakthroughs became paramount not only for winning battles but also for saving lives. In 1940, prior to the United States entering the conflict, a coalition of academic leaders and industrial research labs proposed to President Franklin D. Roosevelt that civilian scientists could be mobilized to create new technologies for military use. This initiative marked a transformative shift in how research was conducted, fostering a collaborative spirit that united the government, universities, and private sector firms in the common goal of advancing medical and technological breakthroughs.
As the war unfolded, the need for innovation quickly became evident. Infectious diseases were a leading cause of death among soldiers, prompting a significant focus on public health solutions. This drive resulted in the establishment of agencies like the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), which coordinated and funded critical wartime research. The successes of this era laid a framework that would support decades of federal funding for research and biomedical partnerships, ultimately shaping the comprehensive U.S. health innovation ecosystem we recognize today.
Impact of WWII on Biomedical Research Partnerships
World War II served as a catalyst for significant advancements in biomedical research, particularly through the formation of public-private partnerships that focused on urgent health needs. The collaborative efforts during this period culminated in groundbreaking innovations, such as the mass production of penicillin, which revolutionized treatments for bacterial infections. As the OSRD spearheaded this initiative, it facilitated a remarkable level of cooperation among federal agencies, universities, and private companies. This collaboration not only addressed immediate concerns but also established a model for future scientific research collaboration that would define American biomedical policy for years to come.
These research partnerships became critical as they allowed for a pooling of resources and expertise that was previously unimaginable. The response to wartime health challenges demonstrated how effective collaboration between federal funding bodies and academic researchers could lead to monumental breakthroughs. Today’s innovation ecosystem in the biomedical field still relies heavily on these foundational partnerships, showcasing how the impacts of past events like WWII continue to shape current health sciences and technologies.
Federal Funding and Its Role in Health Innovation
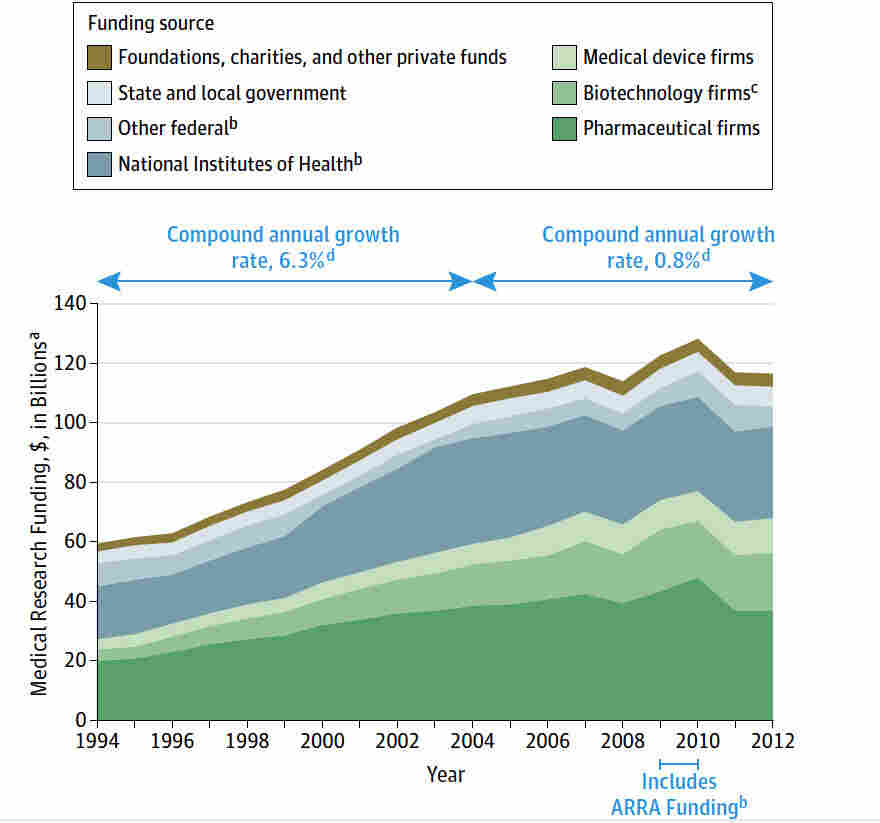
Federal funding has played an essential role in nurturing the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the field of health and biomedical research. Historically, the government’s financial support has been pivotal in facilitating research agendas that align with national interests, from military endeavors to public health crises. The 1940s’ initiatives established a precedent that emphasized the need for sustained investment in scientific research, which has led to substantial advancements in medicine and technology.
However, the conversation around federal funding for research has recently gained traction due to proposed constraints on indirect cost reimbursements. Such changes may undermine the financial stability of research institutions heavily reliant on federal support. This debate highlights the delicate balance that must be maintained to ensure the continued growth and success of the biomedical research partnership, which is critical in driving innovation and addressing current and future health challenges.
Historical Milestones in Health Innovation
Tracing back the historical milestones of U.S. health innovation reveals a narrative intertwined with periods of conflict and national urgency. The advancements in medical science made during World War II, such as the development and mass production of antibiotics like penicillin, not only saved countless lives during the war but set the stage for future achievements in drug development. The collaboration among scientists, scholars, and government entities created an environment ripe for innovation, laying the groundwork for the modern pharmaceutical industry and highlighting the importance of a robust biomedical research framework.
In the following decades, the post-war era saw the expansion of research initiatives supported by federal funding that transformed public health. The establishment of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as a prominent player in biomedical research funding marked a significant shift, enhancing the nation’s capacity to address both emerging and established health issues. Each milestone in this history demonstrates how the underpinning principles of collaborative research and federal support have driven continuous progress in the health innovation ecosystem.
The Role of Scientific Research Collaboration
Scientific research collaboration stands as a core pillar of U.S. health innovation, facilitating advances that might not be possible through isolated efforts. The partnerships formed during WWII between academic institutions and federal agencies exemplified how pooling knowledge and resources could accelerate discoveries. This model of collaboration has evolved into the current ecosystem, where interdisciplinary and cross-sector cooperation is critical for tackling complex health challenges.
Today, this tradition of collaborative research is evident in various aspects of biomedical endeavors, notably in how researchers approach diseases that require multifaceted solutions. The integration of academic research, industry expertise, and federal funding creates a vibrant environment for innovation, continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible in medical science. The enduring legacy of these collaborative efforts underscores their significance in shaping a health innovation landscape that is both dynamic and continuously evolving.
Lessons Learned from Past Health Innovations
Examining the lessons learned from the history of health innovations reveals crucial insights for future endeavors in biomedical research. The extraordinary achievements during WWII, especially regarding efforts like the mass production of penicillin, underscore the importance of rapid response mechanisms to health emergencies. Furthermore, the ability to harness collective expertise through public-private partnerships has proven to be invaluable, ensuring that when faced with dire circumstances, innovation can proceed at an unprecedented pace.
Additionally, the historical context of these innovations offers a framework for assessing contemporary challenges, such as emerging infectious diseases and global health crises. Lessons from past successes can inform current strategies to foster a resilient health innovation ecosystem, emphasizing the need for sustained investment in collaborative research efforts to prepare for future public health needs.
Challenges Facing the Current Health Innovation Ecosystem
Despite its accolades, the U.S. health innovation ecosystem faces several challenges that could impede future advancements. The ongoing discussions surrounding federal funding, particularly the potential cuts to NIH budgets, raise significant concerns about the ability to maintain the research momentum achieved over the past decades. As biomedical research often relies heavily on federal grants, these changes could threaten the stability of research projects and the vitality of emerging scientists in the field.
Additionally, the evolving landscape of public health demands a re-evaluation of existing funding models to ensure that innovation can continue unhindered. With rising costs and increasing complexity in health challenges, addressing these concerns will be crucial to sustaining the robust ecosystem that has made the U.S. a global leader in health innovation.
The Economic Impact of Health Innovations
Health innovations not only transform patient care but also have significant implications for economic growth. The U.S. health innovation ecosystem has positioned the country as a leader in biomedicine, contributing billions to the economy through job creation and industry advancements. Federal funding for research catalyzes private investment, resulting in new technologies and treatments that further enhance healthcare delivery and efficiency.
Innovative solutions in health not only improve patient outcomes but also reduce the long-term economic burden of diseases. Investments in biomedical research yield substantial returns in terms of improved workforce productivity and reduced healthcare costs. Characterizing health innovation as a driver of economic stability reflects a holistic understanding of how advancements in this sector contribute to broader societal welfare.
Future Directions for U.S. Health Innovation
Looking ahead, the future of U.S. health innovation relies on a commitment to sustaining the collaborative frameworks established through decades of successful partnerships. Continued investment in biomedical research, coupled with a focus on fostering innovation across public and private sectors, will be paramount in addressing both current and emerging health challenges. More inclusive policies that support diverse research initiatives can further enhance the nation’s ability to leverage its vast talent pool for future breakthroughs.
Moreover, as global challenges such as pandemics and antibiotic resistance loom, the health innovation ecosystem must adapt its strategies to ensure resilience and responsiveness. Emphasizing adaptability and interdisciplinary collaboration will be critical for driving the next wave of advancements in biomedicine, solidifying the U.S. as a persistent leader in health innovation for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the U.S. health innovation ecosystem and how did it start?
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem refers to the collaborative network of federal funding for research, academic institutions, and private industry that drives advancements in biomedicine and healthcare. It began during World War II when federal support for biomedical research led to breakthroughs such as the mass production of penicillin, establishing a partnership that continues to yield significant health innovations.
How did World War II influence the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
World War II played a crucial role in shaping the U.S. health innovation ecosystem. The urgent need for medical advancements, such as effective treatments for infectious diseases, led to the establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), which fostered public-private partnerships and facilitated significant federal funding for research that laid the groundwork for post-war biomedical advancements.
What is the impact of federal funding for research on the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
Federal funding for research is essential to the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, as it supports academic institutions and encourages collaboration with private industry. These funds have fueled numerous discoveries across medicine and technology, ensuring a steady flow of innovation that enhances healthcare and drives economic growth.
What were the key developments in biomedical research partnerships during the post-World War II era?
Post-World War II, the U.S. health innovation ecosystem saw significant development in biomedical research partnerships. These collaborations between universities, federal research agencies like the NIH, and private companies facilitated groundbreaking discoveries and the establishment of the modern pharmaceutical industry, leading to the drug development advancements we see today.
What challenges does the U.S. health innovation ecosystem face in maintaining its success?
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem faces challenges such as potential federal funding cuts and debates on reimbursement for indirect research costs. Ensuring continued investment and support for public-private partnerships is vital for maintaining the system’s success and ensuring ongoing advancements in biomedical research.
How has the history of health innovation shaped today’s biomedical research landscape in the U.S.?
The history of health innovation, particularly through initiatives from World War II, has shaped today’s biomedical research landscape by establishing a strong foundation of collaboration between the federal government, academia, and private industry. This legacy continues to influence research methodologies, funding structures, and the overall success of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem.
What role does scientific research collaboration play in the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
Scientific research collaboration is a cornerstone of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, facilitating knowledge exchange and resource sharing among universities, government agencies, and private companies. This collaborative approach enhances the efficiency of biomedical research, leading to rapid advancements in medical technologies and treatments.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Origins of the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem | The ecosystem emerged during World War II when the government funded research that led to significant medical breakthroughs, such as mass-producing penicillin. |
| Public-Private Partnership | The collaboration between federal government, academia, and industry has been crucial in advancing biomedical research since the war. |
| Impact of World War II | The urgent health challenges during the war led to innovations that laid the groundwork for modern biomedical research and technology. Infectious diseases posed critical threats, spurring necessary research innovations. |
| Key Transformation | Penicillin’s production methods were established during the war, resulting in a dramatic decrease in disease-related military casualties and initiating a longer-term drug development boom. |
| Continued Success and Critique | Recent debates around federal funding for research, such as proposed cuts to indirect research costs, threaten the ongoing success of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem. |
| Role of New Scientists | The war also served as a training ground for new scientists, contributing to the advancement and diversification of the research workforce in the biomedicine sector. |
Summary
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem is notably recognized as a leader on the global stage. Its origins can be traced back to World War II, where government-sponsored research fostered key developments such as penicillin, setting a precedent for future medical advancements. This partnership between the federal government, academic institutions, and the private sector has led to remarkable innovations that have significantly improved public health and driven economic growth. However, recent proposals to reduce federal funding for biomedical research raise concerns about the sustainability of this successful framework. As the ecosystem continues to evolve, it remains vital to nurture these partnerships to ensure ongoing advancements and maintain the U.S. position at the forefront of health innovation.