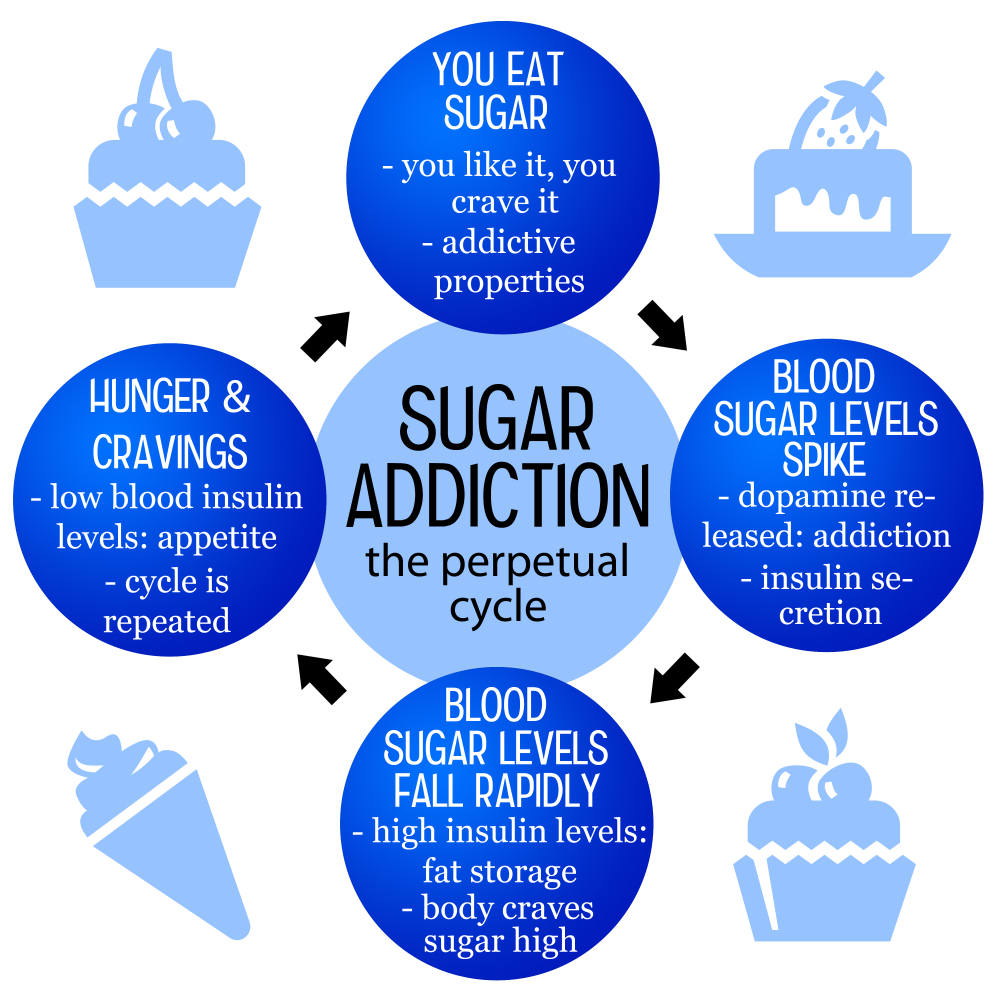
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked a lively debate among nutrition experts, with many asserting that sugar cravings can resemble the compulsive behaviors associated with addiction to substances like alcohol or nicotine. Our modern food system is inundated with processed foods that are laden with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which often heighten these cravings and lead to habitual consumption. While sugar can trigger withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when cut out abruptly, it’s crucial to differentiate between sugar and clinically recognized addictive substances. Understanding the health effects of sugar is essential, as moderate intake, particularly in the form of natural sugars from fruits and whole grains, can be beneficial. Thus, while sugar may share some qualities with addictive substances, it is essential to approach this topic with nuance, recognizing both its pleasures and the risks associated with excessive consumption.
When contemplating the nature of sweeteners, one might wonder if the consumption of sugary substances resembles that of addictive behaviors typically linked to drugs or alcohol. Terms like sugar dependence or sugar habit can evoke the idea of an ingrained dietary pattern influenced by highly palatable processed foods, which are notoriously rich in added sugars. The discussion surrounding diet and sugar has gained traction, highlighting concerns about the impact of excessive sugar intake on overall health. With increased awareness regarding sugar addiction, it’s important to acknowledge how the modern diet is often compromised by the prevalence of hidden sugars in common foods. Exploring this topic reveals the complexities of cravings and the need for a balanced approach to sweetness in our lives.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked significant debate among health professionals. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are officially classified as addictive, the same criteria do not apply to sugar. Research suggests that sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, akin to those experienced with addictive drugs. This is largely due to the ultra-processed foods often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and salt, which can lead to a cycle of excessive consumption and subsequent withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced. When someone decides to eliminate these foods from their diet, they may face challenges such as headaches and anxiety, pointing to a complex relationship with sugar that resembles addiction.
Despite these qualities, it’s crucial to differentiate between necessary nutrients and addictive substances. For instance, our bodies need sugar for energy and it naturally occurs in many healthy foods like fruits and dairy. The average American’s sugar intake, particularly from added sugars in processed foods, has reached alarming levels, with recommendations suggesting a limit far lower than current consumption. The key takeaway for individuals looking to manage their sugar intake lies in moderation. By understanding the nuances of sugar’s role in our diets, one can work on cravings without completely eliminating all forms of sugar, thus avoiding counterproductive withdrawal responses.
Health Effects of Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption has profound health implications. High intake is associated with a range of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to prevent these adverse effects, emphasizing that while sugar can enhance the flavor of foods, its overconsumption is detrimental. Continuous high sugar intake leads to insulin resistance and can overwhelm the body’s metabolic machinery. Understanding these health effects is essential for making informed dietary choices and maintaining overall health.
Additionally, reducing sugar intake can improve not only physical health but also mental well-being. Studies indicate that high sugar diets can negatively influence mood and cognitive function. As individuals begin to wean off processed foods high in sugar, many report feeling more energetic and experiencing improved mental clarity. This highlights the importance of dietary choices in both physical and psychological health, encouraging a balanced approach to sugar that promotes a healthier lifestyle and well-being.
Recognizing the health risks associated with sugar is vital in today’s society where processed foods dominate the market. Not only should consumers be mindful of the direct health effects, but they should also cultivate awareness around hidden sugars in food products, as this knowledge is fundamental to making healthier dietary choices.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Navigating sugar cravings is a complex endeavor, particularly in a world filled with tempting processed foods. It’s important to recognize that while cravings may feel uncontrollable, they can be effectively managed. Strategies such as gradually reducing sugar intake rather than going cold turkey can help mitigate withdrawal symptoms. Simple practices like reading food labels can make a significant difference, as people become more aware of hidden sugars in snacks and beverages. Making small, consistent changes can lead to lasting habits, thereby lessening the frequency of sugar cravings over time.
Incorporating wholesome foods into daily meals can also combat sugar cravings. Choosing whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can provide essential nutrients and fiber, which help regulate blood sugar levels and increase satiety. Furthermore, engaging in mindful eating practices, like savoring each bite and appreciating the flavors of healthy foods, can refocus attention away from sugary snacks. These methods not only diminish the desire for sugar but can also promote a healthier relationship with food. Balancing dietary needs without extreme restriction is key to long-term success.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Intake
Processed foods have revolutionized our diets but come at a cost, particularly concerning sugar consumption. Many of these products contain high levels of added sugars, which can lead to both physical dependency and adverse health effects. When individuals consume excessively processed items, the high sugar content can trigger intense cravings and promote overeating. Recognizing the prevalence of sugar in our diets demands a critical approach to food choices, urging consumers to opt for fresher, less processed alternatives.
Moreover, the relationship between processed food and sugar intake reveals the systemic nature of dietary health. Individuals often resort to processed foods for convenience, leading to a cycle where quick meals become a staple. However, this is where knowledge and education about food sourcing and cooking can make a significant impact. By prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can enjoy the natural sugars present in fruits and dairy, thus satisfying cravings without the detrimental effects of added sugars. Cultivating awareness around food processing and its implications on sugar consumption is pivotal for a healthier community.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar in Your Diet
Successfully reducing sugar in one’s diet involves implementing practical strategies that promote gradual change rather than drastic measures. Individuals can start by replacing sugary snacks with healthier options such as fruits, nuts, or yogurt to fulfill cravings without the excess sugar. Additionally, cooking meals at home allows for greater control over ingredients, minimizing added sugars present in restaurant and pre-packaged foods. As people become more mindful of what they consume, they can significantly lower their total sugar intake over time.
Moreover, understanding the common sources of sugar in everyday items can empower consumers to make smarter choices. For instance, beverages like soda and energy drinks can be significant contributors to daily sugar consumption. Opting for water or unsweetened alternatives is an effective step toward reducing sugar intake. Education about reading labels and identifying hidden sugars is crucial. By learning to recognize terms like high fructose corn syrup and cane sugar, consumers can navigate product choices more effectively and work towards a diet that supports better health outcomes.
The Psychological Impact of Sugar on Eating Behaviors
Sugar consumption can have a profound psychological effect, influencing eating behaviors and cravings. For many individuals, the instant gratification provided by sugary foods creates a pattern of reward and reinforcement in the brain, similar to that seen with addictive substances. This phenomenon underscores why some individuals find it difficult to resist sugar-laden treats and can lead to a cycle of dependency. Understanding these psychological triggers can lead to more effective strategies for managing cravings and making healthier choices.
Additionally, the psychological impact of sugar doesn’t just end with cravings; it can also contribute to guilt and shame in relation to food choices. Many people feel overwhelmed by the pressure to adhere to strict dietary guidelines, only to give in to sugar cravings. This can lead to an unhealthy cycle of restriction followed by binge eating, particularly with sweets. A more compassionate approach to dietary habits, focusing on balance and self-acceptance, can foster a healthier relationship with sugar, allowing individuals to enjoy treats in moderation without guilt.
Long-Term Consequences of High Sugar Intake
Long-term consumption of high sugar diets has been linked to a myriad of health conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Continuous high intake contributes to metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. These alarming statistics illustrate the importance of reconsidering dietary choices that prioritize high sugar levels, particularly from processed foods. Understanding these long-term consequences is crucial for individuals aiming to shift their eating habits for better health outcomes.
In addition to physical health consequences, high sugar intake can have a lasting impact on mental health as well. Emerging research indicates a link between sugary diets and mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. The sugar-dependent cycle can lead to fluctuations in mood, worsening overall psychological wellbeing. As awareness grows, it’s evident that reducing sugar intake not only safeguards physical health but also enhances mental wellness. Prioritizing dietary changes aimed at lowering sugar consumption could significantly benefit both mind and body in the long run.
The Importance of Balanced Sugar Consumption
Finding balance in sugar consumption is essential for maintaining health without feeling deprived. While completely eliminating sugars from the diet is neither practical nor necessary, moderation is key. Properly integrating natural sugars found in fruits and other foods can allow individuals to enjoy the sweetness they crave while reaping the benefits of essential vitamins and minerals. By focusing on balance, one can avoid the risks associated with excessive sugar while satisfying their taste preferences.
Education about sugar consumption helps individuals recognize that it’s not just about quantity, but also quality. Choosing items with naturally occurring sugars and avoiding those laden with added sugars can make a significant difference. Encouraging a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods will not only curtail the intake of excess sugars but enhance overall nutritional quality. This balanced approach ultimately nurtures a healthier relationship with food, allowing individuals to enjoy sweet flavors mindfully, rather than succumbing to sugar cravings.
Mindful Eating and Cravings Management
Mindful eating practices can play a vital role in managing sugar cravings effectively. This approach encourages individuals to cultivate awareness around their eating habits, which helps identify triggers for cravings. By eating slowly and savoring every bite, people can enhance their food experience and make more conscious choices about what they consume. This mindfulness helps in acknowledging cravings without necessarily yielding to them, allowing for healthier dietary decisions.
Incorporating mindful practices into daily life can also improve emotional health. Often, individuals eat sugary foods in response to stress or boredom. Mindfulness encourages a pause, enabling people to assess their emotions and their real hunger levels before reaching for food. Such awareness can lead to better coping strategies and reduced reliance on sugar for comfort. Adopting mindful eating can create a more balanced relationship with food, ultimately diminishing the power of sugar cravings and supporting healthier lifestyle choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar has addictive qualities similar to more commonly recognized substances like alcohol and nicotine, it is not classified as an addictive substance in clinical terms. Sugar can create cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, particularly through ultra-processed foods that contain added sugars.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to various health issues, including weight gain, increased cravings, and withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when consumption is reduced. However, moderate intake of sugar, especially from natural sources, does not generally lead to severe health consequences.
How do sugar cravings affect our diet?
Sugar cravings can greatly influence dietary choices, often leading individuals to prefer processed foods rich in sugar. These cravings can create a cycle of habitual consumption that may be challenging to break, hence the importance of monitoring sugar intake.
Are processed foods responsible for sugar addiction?
Yes, processed foods are a significant contributor to sugar cravings and potential sugar addiction. They often contain high levels of added sugar and unhealthy fats, which enhance palatability and can lead to overeating.
What role does sugar play in a balanced diet?
Sugar can enhance flavor and texture in foods, and an appropriate amount can contribute positively to our diet. However, it’s essential to limit added sugars to maintain health and avoid the negative consequences associated with excessive sugar consumption.
Can reducing sugar in my diet cause withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, abruptly reducing sugar intake can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. It’s recommended to gradually decrease added sugar consumption instead of going cold turkey to minimize these effects.
What is the recommended daily intake of sugar for adults?
The American Heart Association recommends that men limit their intake of added sugars to no more than 9 teaspoons per day, and women to no more than 6 teaspoons, with lower amounts recommended for children.
How can I manage my sugar intake effectively?
To manage sugar intake effectively, read nutrition labels, become aware of hidden sugars in processed foods, and gradually reduce added sugars in your diet. This mindful approach can help break the cycle of cravings and promote healthier eating habits.
Why do we need sugar in our diet?
We need some sugar in our diet as it provides energy and enhances the taste of foods. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are important components of a balanced diet.
Is all sugar bad for you?
Not all sugar is bad for you; naturally occurring sugars found in whole foods like fruits and vegetables are beneficial and part of a healthy diet. The focus should be on minimizing added sugars found in processed foods to prevent health issues.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sugar and Addiction | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating behaviors but is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms can occur when stopping ultra-processed foods, but the intensity is lower than that of addictive drugs. |
| Sugar in Our Diet | Sugar is found in essential foods such as fruits and dairy; eliminating it entirely is not feasible or necessary. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The average U.S. adult consumes about 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, greatly exceeding the recommended 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
| Moderation is Key | Low to moderate amounts of sugar can enhance the diet; it’s important to reduce sugar gradually rather than eliminating it abruptly. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a complex topic debated among nutrition experts. While sugar does create cravings and may lead to compulsive eating, it is not officially an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Understanding the role of sugar in our diets is crucial; it provides necessary energy found in many whole foods. Rather than viewing sugar through the same lens as addictive drugs, moderation and awareness of sugar intake are key to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The importance of not overconsuming added sugars cannot be overstated, given the typical American diet’s excess. Thus, while sugar has addictive qualities, its presence in our diet is essential and should be managed wisely.