U.S. maternal mortality has reached alarming levels, reflecting a public health crisis that cannot be ignored. Despite advancements in medical technology and prenatal care, an astonishing number of pregnancy-related deaths in the nation are preventable, highlighting significant gaps in maternal health services. From 2018 to 2022, the maternal mortality rate has not only remained the highest among high-income countries but has also shown troubling increases, particularly among marginalized communities. This pressing issue calls for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care to address the systemic health disparities that contribute to rising mortality rates. As we look deeper into the factors at play, it becomes clear that improving U.S. maternal mortality is crucial for safeguarding future generations of mothers and infants alike.
The ongoing crisis surrounding maternal health in the United States has prompted urgent discussions about pregnancy outcomes and the alarming rates of maternal deaths. In particular, the term ‘maternal mortality’ encompasses a range of related concepts, such as pregnancy-related complications, postpartum health issues, and disparities in healthcare access. As the nation grapples with these challenges, the pressing need for quality maternal care becomes increasingly evident. Addressing the factors contributing to these negative outcomes, including inadequate prenatal care and the lack of support during the postpartum period, is essential for fostering a healthier future for mothers and their children. The discourse surrounding maternal health has evolved, urging policymakers and healthcare providers to prioritize effective solutions to combat these persistent issues.
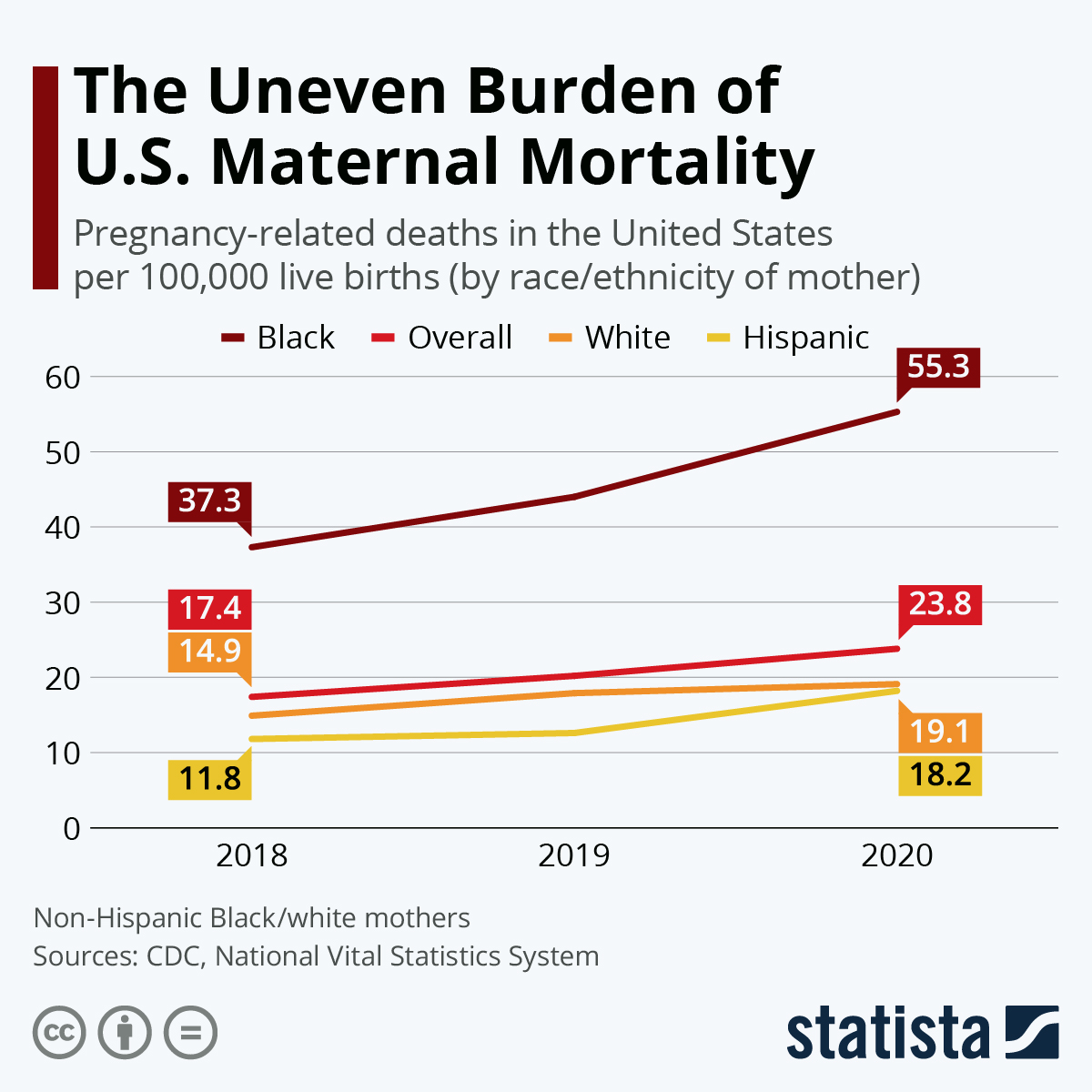
The Alarming Rise of U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
The ongoing rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates, particularly during pregnancy and the postpartum period, poses a grave public health concern. Between 2018 and 2022, research indicates that these rates increased from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births to 32.6, signifying a troubling trend that places the U.S. at the forefront of maternal mortality among high-income countries. Issues such as inadequate prenatal care, systemic racism, and disparities in healthcare access play a significant role in these rising statistics. It is imperative that we understand the factors leading to preventable pregnancy-related deaths if we hope to implement effective changes in maternal health policies and practices across the nation.
The statistics surrounding U.S. pregnancy-related deaths reveal a stark reality: over 80% of these fatalities could potentially be averted with better healthcare access and support. Researchers point out that maternal mortality rates differ dramatically across racial and ethnic groups, showcasing a critical need for targeted interventions. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face nearly four times higher mortality rates compared to their white counterparts. This disparity in maternal health outcomes underscores the urgent necessity for comprehensive solutions that address both prenatal and extended postpartum care, ensuring equitable healthcare for all mothers regardless of race or location.
Understanding Health Disparities in Maternal Health
Health disparities are a pressing issue in maternal health, often leading to inequitable outcomes for diverse populations. Racial and ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Indigenous women, are disproportionately affected by higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Factors such as living in maternity care deserts, which lack adequate healthcare facilities and resources, exacerbate these disparities. Systemic issues, including socioeconomic barriers and insufficient insurance coverage, are also pivotal in determining access to quality prenatal care, directly impacting maternal health outcomes.
In the fight against maternal mortality, it is essential to recognize and address the systemic inequalities that exist within the healthcare system. Despite innovations to mitigate racial inequities, a significant gap remains. This highlights the need for policies that effectively tackle the social determinants of health and prioritize equitable prenatal care for marginalized groups. By focusing on both prevention and intervention, we can begin to close the gap in maternal health disparities and work towards a more just healthcare system.
Tackling these disparities calls for a multifaceted approach that includes increased funding for community health programs, ongoing training for healthcare providers to combat implicit bias, and an emphasis on culturally competent care. As we develop strategies to improve maternal health, it is crucial to involve the affected communities in the dialogue, ensuring their experiences and insights shape the solutions we pursue.
The Importance of Comprehensive Prenatal Care
Comprehensive prenatal care is vital for preventing pregnancy-related deaths and fostering maternal health. Ensuring expectant mothers receive timely and well-structured care throughout their pregnancies helps identify and manage complications early. Access to regular check-ups, screenings, and educational resources equips mothers with the information and support needed to navigate their pregnancies safely. Furthermore, prenatal care serves as a gateway to addressing underlying health conditions that may impede maternal and fetal health, such as untreated hypertension or diabetes.
However, despite its importance, many women face significant barriers to accessing quality prenatal care, including financial constraints and geographical limitations. Enhanced policies that prioritize the expansion of accessible and affordable prenatal services are needed to address these challenges. Community-based health initiatives, mobile clinics, and telehealth services can bridge the gap for underserved populations, ensuring that all mothers receive the comprehensive care required for a healthy pregnancy.
Addressing Postpartum Care Challenges
Postpartum care represents a critical but often overlooked area of maternal health. The findings from recent studies reveal that nearly a third of maternal deaths occur during the late postpartum period, emphasizing the necessity of ongoing support beyond the traditional six-week check-up. Women require continuous monitoring and resources during their recovery phase to address potential complications and mental health challenges that can arise after delivery.
Recognizing postpartum care as an extension of maternal health services is vital for improving outcomes. Health systems must adapt to provide comprehensive programs that include postpartum check-ups, mental health support, and education about recovery. By expanding the understanding of postpartum health and addressing the barriers women face during this period, we can significantly decrease the rates of maternal mortality and enhance overall maternal well-being.
Innovative Solutions to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
Innovation plays a crucial role in improving maternal health outcomes in the U.S. By adopting new technologies and collaborative care models, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of prenatal and postpartum services. For example, integrating telehealth into maternal care allows healthcare providers to reach women who may otherwise lack access to essential services due to distance or financial limitations.
Moreover, leveraging data analytics to monitor maternal health trends can help identify at-risk populations and inform targeted interventions. Collaborative initiatives between state health departments, community organizations, and healthcare providers can facilitate comprehensive care models that address the diverse needs of mothers throughout their pregnancy journey. Such innovative approaches not only improve access and quality but also help reduce the alarming rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
The Role of Policy Change in Maternal Health Improvement
Policy change plays a pivotal role in driving improvements in maternal health care. To tackle the rising trend of maternal mortality, policymakers must focus on addressing the root causes of health disparities and ensuring access to quality care for all women. This includes advocating for legislative measures that expand insurance coverage for maternal services, increase funding for maternal health programs, and support initiatives aimed at addressing social determinants of health.
Furthermore, engaging stakeholders, including healthcare providers, community organizations, and maternal health advocates, is essential for developing effective policies. By fostering collaborative efforts, states can learn from one another’s successes and failures, creating a roadmap to improved maternal health outcomes. Ultimately, comprehensive policy reforms will aid in creating systemic changes necessary to tackle the persistent issues surrounding maternal mortality in the U.S.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions on Maternal Mortality
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease have a profound impact on maternal mortality rates. Over the years, the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. has shifted towards cardiovascular issues, highlighting the need for early detection and management of these conditions before, during, and after pregnancy. Understanding the relationship between chronic health conditions and maternal mortality helps underscore the importance of comprehensive preconception care and regular monitoring for women with pre-existing health issues.
Addressing chronic conditions in reproductive-age women is paramount for reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Health systems should prioritize screening and educating women about how pre-existing health conditions can affect their pregnancies. Moreover, integrating care teams that focus exclusively on the needs of pregnant women with chronic conditions can lead to better health outcomes, ultimately reducing mortality rates and improving the quality of life for mothers.
The Need for Improved Data Collection in Maternal Health
Evidence-based approaches to improving maternal health rely heavily on accurate and comprehensive data collection. The U.S. faced significant challenges in tracking maternal deaths due to inconsistent data reporting methods until the introduction of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018. Accurate data not only highlights the scale of the maternal mortality crisis but also informs targeted interventions and policies that can drive improvements in maternal health.
Expanding maternal health data collection efforts to include demographics, geographic factors, and health outcomes will provide a clearer picture of the disparities present in maternal care. This information can help identify vulnerable populations, evaluate the effectiveness of existing programs, and shape future health initiatives. As the United States seeks to address the rates of pregnancy-related deaths, investing resources into robust data systems will be crucial for tracking progress and making informed decisions.
Advocating for Access to Quality Maternal Healthcare
Access to quality maternal healthcare is a fundamental right that remains out of reach for many women in the U.S. Advocacy is essential for reshaping the conversation around maternal health, driving policy changes, and ensuring equitable access to necessary resources. Grassroots efforts, led by mothers and community organizations, can amplify voices that have long been marginalized in discussions about healthcare access and maternal rights.
Through advocacy, communities can push for increased funding for maternal health initiatives, comprehensive insurance coverage, and the elimination of systemic barriers that hinder access to care. By creating awareness of the challenges faced by pregnant women and new mothers, we can collectively work towards a future where all women receive the support they need to thrive during pregnancy and postpartum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of U.S. maternal mortality?
The main causes of U.S. maternal mortality include chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, which accounted for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. Other significant contributors are hemorrhage, pre-eclampsia, and conditions arising during the postpartum period. Addressing these issues through better healthcare access and prenatal care can help reduce mortality rates.
How can maternal health disparities impact U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities significantly impact U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, with racial and ethnic groups, particularly American Indian and Alaska Native women, facing disproportionately high mortality rates. These disparities are influenced by factors like socioeconomic status, access to quality prenatal care, and systemic bias within healthcare, highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
Why is extended postpartum care important in reducing maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Extended postpartum care is crucial in reducing U.S. maternal mortality as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Recognizing the postpartum period as a continuum rather than a fixed duration ensures that mothers receive the necessary health support beyond the traditional six-week check-up, directly impacting maternal health outcomes.
What role does prenatal care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Prenatal care plays a vital role in preventing pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. by enabling early detection and management of potential pregnancy complications. Comprehensive prenatal services enhance maternal health, reduce risks associated with chronic conditions, and ensure that expectant mothers receive guidance throughout their pregnancy, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
How do health disparities across states affect national maternal mortality rates?
Health disparities across states directly affect national maternal mortality rates, as some states report significantly higher rates than others. Factors such as access to healthcare, socioeconomic conditions, and state-level policies contribute to these variations. Addressing these disparities through uniform health policies and improving prenatal and postpartum care access can help achieve better national outcomes.
What improvements are necessary to combat rising U.S. maternal mortality rates?
To combat rising U.S. maternal mortality rates, improvements are necessary in public health infrastructure, access to comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care, and addressing systemic inequities in the healthcare system. Increased investment in maternal health initiatives and policies that support vulnerable populations are critical for enhancing health outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with a rate of 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Disparities in Maternal Mortality | Significant racial disparities exist, with American Indian/Alaska Native women at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared to 27.6 for white women and 76.9 for non-Hispanic Black women. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The highest increase in mortality rates occurred in 2021, likely due to the pandemic, with overall rates still elevated after the pandemic’s onset. |
| Leading Causes of Maternal Death | Cardiovascular disease accounts for over 20% of deaths, marking a shift from hemorrhage being the leading cause. |
| Importance of Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth, suggesting a need for healthcare focus beyond the immediate postpartum period. |
| Need for Improved Care | The study suggests investing in public health infrastructure and addressing healthcare inequities is essential to reduce maternal mortality. |
Summary
U.S. maternal mortality remains a pressing concern, with preventable deaths continuing to rise in the nation. As studies reveal significant racial and state disparities, it is critical to address the systemic issues within the healthcare system. With the leading causes identified and the importance of postnatal care acknowledged, a comprehensive approach that includes better prenatal services and ongoing healthcare support can help reverse this alarming trend. Efforts must focus on policy improvements and investment in healthcare infrastructure to ensure that maternal health outcomes are prioritized and improved for all women.