Bile acid imbalance plays a critical role in the development of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma, the most prevalent type of liver cancer. This imbalance occurs when the delicate regulation of bile production by the liver is disrupted, leading to the overproduction of bile acids that can cause liver injury and inflammation. Recent research highlights the importance of molecules like the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) in maintaining bile acids’ functional balance, underscoring their influence on liver function. The findings reveal a profound connection between metabolic control, bile acids, and cancer progression, paving the way for novel therapeutic interventions in liver disease. As scientists continue to explore this complex relationship, addressing bile acid imbalance may become crucial in combating liver cancer and enhancing overall metabolic health.
The disruption of bile acids homeostasis is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the onset of liver-related disorders, particularly in the context of liver malignancies. This phenomenon, often referred to as bile acid dysregulation, sheds light on the underlying mechanisms linking liver function and cancer development, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Through mechanisms involving hormones like FXR, bile acids not only assist in fat digestion but also play a pivotal role in various metabolic pathways that influence tumor dynamics. Understanding these interactions raises important implications for how we can manipulate bile metabolism to develop new treatment modalities for liver diseases. As research progresses, the focus on bile acid imbalances may reveal groundbreaking insights into liver health and cancer prevention strategies.
Understanding Bile Acids and Their Role in Liver Function
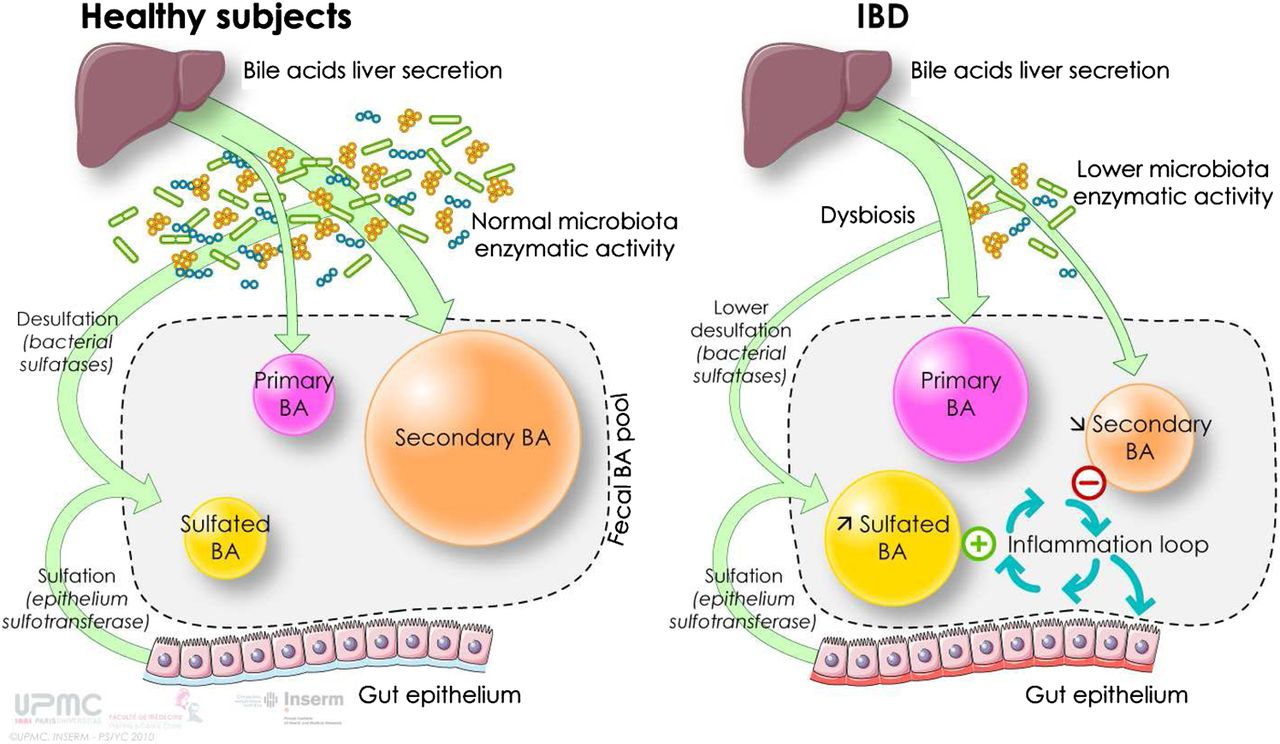
Bile acids are synthesized in the liver and play a pivotal role in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. They are derived from cholesterol and are secreted into the bile, subsequently stored in the gallbladder until needed during digestion. Beyond their well-known detergent-like capabilities, bile acids exert hormonal functions, influencing various metabolic pathways in the body. This metabolic control is particularly vital for maintaining proper liver function, as imbalances in bile acid levels can lead to several liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Moreover, the interaction of bile acids with the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a key nuclear receptor in the liver, highlights their significance in maintaining hepatic homeostasis. FXR regulates bile acid synthesis, promoting a balance that prevents the over-accumulation of bile acids, which can be detrimental. Disruptions in this balance can initiate liver injury and inflammation, escalating the risk of liver cancer, particularly HCC. This intricate relationship underscores the necessity of understanding bile acid metabolism in the context of liver health.
Bile Acid Imbalance Linked to Liver Cancer
Recent research has unveiled a critical link between bile acid imbalance and the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When the regulation of bile acids, particularly through the action of the FXR, is disrupted, bile acids can accumulate excessively in the liver. This toxic build-up triggers inflammation and fibrosis, setting the stage for tumor development. The study led by Yingzi Yang emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper bile acid levels to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting how a slight imbalance can escalate into severe liver disease.
In the context of cancer metabolism, bile acids serve as crucial signaling molecules that coordinate various metabolic functions. The hyperactivation of pathways like Hippo/YAP can lead to the suppression of FXR, exacerbating the overproduction of bile acids. This knowledge could pave the way for innovative treatment strategies aimed at restoring bile acid balance, either by enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion to mitigate liver damage and combat cancer progression. Such therapeutic interventions may significantly alter the prognosis for patients at risk of developing liver cancer.
Investigating the relationship between bile acid metabolism and liver cancer can unlock new potential treatments. By focusing on pharmacological approaches that stimulate FXR, researchers may devise interventions that not only treat but also prevent the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the molecular mechanisms at play in bile acid imbalance will be vital in developing effective therapeutic solutions that can alter the trajectory of liver disease.
The Role of FXR in Liver Disease Management
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is integral to bile acid signaling and metabolism. Its role extends beyond bile acid homeostasis to encompass broader metabolic control within the liver. Dysregulation of FXR has been linked to various liver diseases, including steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. By engaging with bile acids, FXR helps to regulate lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory processes, making it a focal point in the management of liver diseases.
Research advances indicate that enhancing FXR function may serve as an effective therapeutic target for liver cancer prevention and treatment. Approaches that activate FXR could not only restore proper bile acid levels but also reduce liver inflammation and subsequent fibrosis. Such findings open promising avenues for developing new pharmacological treatments aimed at mitigating the risks associated with liver cancer, providing hope for individuals affected by liver dysfunction due to bile acid imbalances.
Cell Signaling Pathways in Liver Cancer Progression
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway plays a significant role in liver cancer progression, especially in regulating cell growth and proliferation. Recent studies suggest that YAP, typically known for promoting growth, can paradoxically act as a repressor within bile acid metabolism. By inhibiting FXR’s function, YAP contributes to an overproduction of bile acids, leading to liver inflammation and increased susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing strategies to counteract its detrimental effects.
Targeting the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway offers a novel approach to disrupt the cycle of bile acid excess and liver damage. By inhibiting YAP’s repressive influence on FXR, researchers can potentially enhance bile acid regulation, thus reducing liver fibrosis and lowering the risk of tumor development. This intersection of metabolic control and cancer biology highlights the necessity for comprehensive research focused on cell signaling mechanisms that may unlock transformative treatment options for liver diseases.
Metabolic Control in Cancer: The Bile Acid Connection
Metabolic control is increasingly recognized as a vital factor in cancer biology, with bile acids emerging as key players in this complex interplay. The ability of bile acids to influence metabolic pathways underscores their importance not only in digestion but also in cell signaling related to cancer growth. Alterations in bile acid metabolism can disrupt this delicate balance, potentially leading to the pathogenesis of liver cancer, particularly HCC. Exploring the metabolic roles of bile acids may offer insights into how cancer cells adapt to their environment.
Research indicates that certain bile acids might promote a favorable metabolic state for tumor development, while others play a protective role against cancer progression. Understanding the dual nature of bile acids as both signaling molecules and metabolic regulators is essential for devising interventions aimed at correcting bile acid imbalances in cancer patients. Fostering metabolic control through bile acid regulation presents a promising frontier in therapeutic strategies against liver cancer.
Potential Therapeutic Avenues in Liver Cancer Treatment
The identification of bile acid imbalances as a contributing factor to liver carcinogenesis has spurred interest in potential therapeutic interventions. Enhancing FXR activity presents a promising strategy to restore bile acid homeostasis and mitigate liver inflammation, which are crucial for preventing the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacological agents that promote FXR function or improve bile acid excretion could prevent the toxic accumulation of bile acids, thereby reducing the risk of tumor formation.
In addition, understanding how to manipulate bile acid pathways may provide a broader array of treatment options. Approaches such as using bile acid sequestrants to reduce their absorption can also be explored as a means to prevent excess bile acid buildup. As research continues to unveil the complexities of bile acid signaling and its impact on liver health, clinicians may find new avenues for combatting liver cancer, uniquely tailored to address the underlying metabolic dysregulation.
The Interplay Between Nutrition and Bile Acid Metabolism
Nutritional factors play a profound role in bile acid metabolism, influencing the production and regulation of these vital substances in the liver. Dietary components, such as fiber and certain lipids, can affect bile acid synthesis and composition, thereby impacting overall liver health. A diet high in fiber may promote probiotics that enhance bile acid excretion, which is key in preventing bile acid-induced inflammatory conditions and liver cancer.
Moreover, understanding how specific diets influence bile acid composition could lead to dietary interventions for individuals at risk of liver diseases. Personalized nutrition strategies that align dietary patterns with bile acid management might effectively reduce liver cancer risk by restoring balance to bile acid levels. Continued exploration into the dietary influences on bile acid metabolism could yield actionable insights for preventing hepatocellular carcinoma and supporting liver health.
Implications of Bile Acid Research on Liver Health
The implications of bile acid research extend far beyond the realm of liver cancer, shedding light on various liver diseases and overall metabolic health. By comprehensively understanding the roles of bile acids in liver function, researchers can identify novel biomarkers for liver diseases and develop targeted therapies. This growing knowledge base is essential for elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for liver injuries and cancers, potentially leading to groundbreaking approaches in medical treatment.
Moreover, as research into bile acids and their systemic effects progresses, the potential for translating these findings into clinical practice becomes increasingly tangible. Understanding bile acid signaling pathways will guide the development of diagnostic tools and therapies aimed at improving liver health outcomes. As interest in this field continues to expand, it is likely that targeting bile acid metabolism will emerge as a core strategy in combating liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma.
Future Directions in Bile Acid and Cancer Research
Looking ahead, future research into bile acids and their relationship with liver cancer holds exciting potential for unveiling new therapeutic strategies. Investigating the nuances of bile acid metabolism can help clarify how these compounds modulate various aspects of cellular signaling and metabolic control within the liver. By focusing on the mechanisms by which bile acids influence cancer progression, researchers can identify new targets for intervention that may disrupt the cycle of liver disease and malignancy.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary approaches combining molecular biology, nutritional science, and pharmacology could enhance our understanding of bile acid dynamics. Collaborations in research may broaden the scope of treatment paradigms for liver diseases, integrating dietary management with molecular therapies targeting bile metabolism. By fostering innovative study designs, the potential to develop effective solutions for liver cancer will grow, ultimately improving patient outcomes and advancing liver health worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is bile acid imbalance and how is it linked to liver function?
Bile acid imbalance refers to the disruption in the production and regulation of bile acids, which are crucial for fat digestion and various metabolic processes in the liver. This imbalance can lead to liver dysfunction, inflammation, and conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer.
How can bile acid imbalance trigger liver cancer development?
The accumulation of bile acids due to an imbalance can cause liver injury and inflammation. In particular, the dysregulation of bile acid metabolism can paralyze essential receptors like FXR, leading to fibrosis and increasing the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as a consequence of ongoing liver damage.
What role does the YAP protein play in bile acid metabolism and liver disease?
YAP plays a dual role in liver biology by promoting tumor formation and regulating bile acid metabolism. In cases of bile acid imbalance, YAP acts as a repressor of FXR, a vital bile acid sensor, leading to overproduction of bile acids, liver inflammation, and potentially contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development.
Can targeting bile acid receptors like FXR be a therapeutic strategy for liver cancer?
Yes, enhancing FXR function could represent a promising pharmacological approach to correcting bile acid imbalance and mitigating liver damage. By stimulating FXR or promoting bile acid excretion, researchers hope to reduce inflammation and limit the progression of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What are the implications of bile acid imbalance for metabolic control in cancer?
Bile acid imbalance not only affects liver function but also plays a significant role in metabolic control, influencing nutrient sensing pathways that could impact cancer progression. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism may therefore contribute to metabolic dysregulation commonly observed in cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
How does liver inflammation from bile acid imbalance contribute to liver cancer risk?
Chronic liver inflammation caused by bile acid imbalance can lead to scarring and fibrosis. Over time, this persistent inflammation heightens the risk of mutations and cellular changes that increase the likelihood of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), highlighting the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis for liver health.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Bile Acid’s Role | Bile acids, produced by the liver, aid in fat digestion and have a hormone-like function that regulates metabolic processes. |
| Imbalance Consequences | An imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver injury, inflammation, and lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Key Molecular Findings | The study identified YAP, a key molecular switch, as a repressor of bile acid metabolism by interfering with FXR, crucial for bile acid homeostasis. |
| Potential Treatments | Potential pharmacological interventions may include stimulating FXR or enhancing bile acid excretion to reduce cancer progression. |
Summary
Bile acid imbalance is a critical health issue linked to liver cancer, as revealed by recent research. The study highlights how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to significant liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the molecular mechanisms involved, such as the role of YAP and FXR, opens the door to potential treatment strategies that could mitigate liver damage and progress towards better health outcomes.